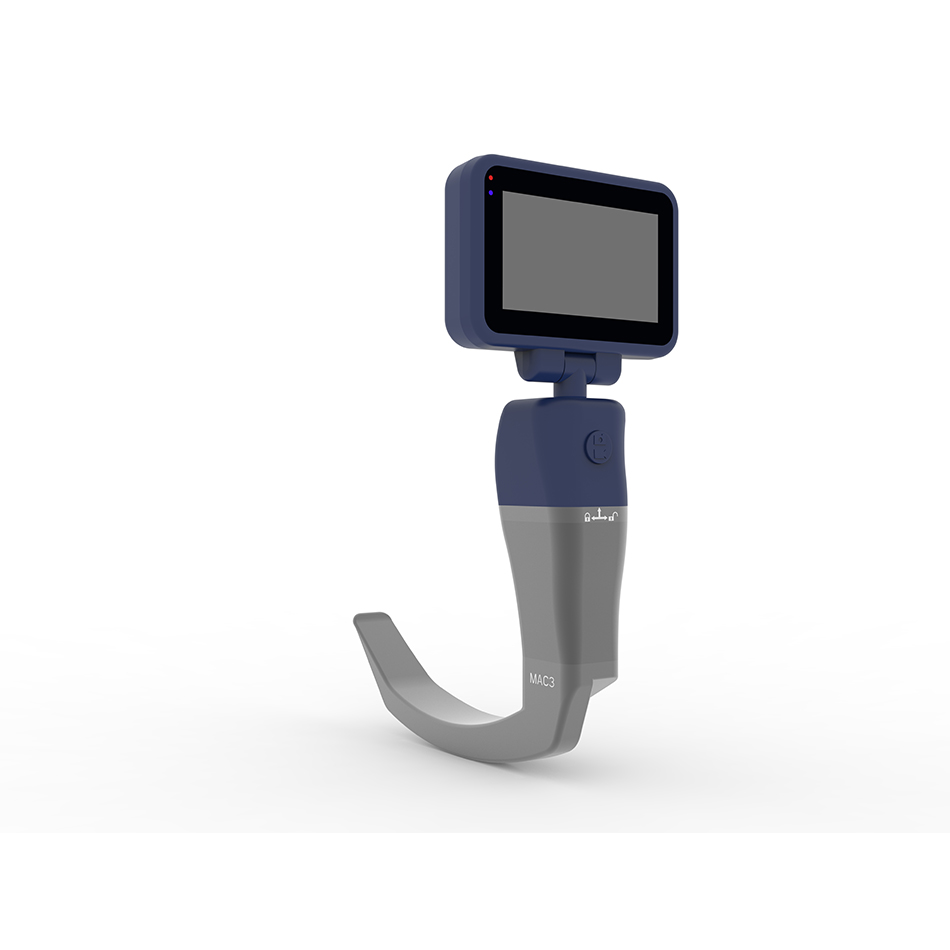
Medical total video laryngoscope
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
There are two laryngoscopes: indirect laryngoscope and direct laryngoscope. The two have different usage modes and scope of application, respectively. Indirect laryngoscopy is the most commonly used in laryngeal examination, and the mirror diameter can be selected according to the patient's pharyngeal cavity, and the entire larynx can be examined regionally by its slow rotation.


Indirect laryngoscopy is simple and easy for doctors to master and is less painful for patients, but it should not be used in patients with sensitive gag reflexes as well as in patients with tongue base hypertrophy and poor epiglottic lifting.
Direct laryngoscopy is not a routine examination of the larynx because it causes some trauma to the patient to varying degrees. Direct laryngoscopy is indicated when indirect laryngoscopy and fiberoptic laryngoscopy are unsuccessful, and tissue biopsy specimens from the larynx can be taken. Direct laryngoscopy can be used in the treatment of laryngeal lesions, such as electrocautery, benign tumor resection, local medication and removal of laryngeal foreign bodies, and can also be used for bronchoscopy, endotracheal anesthesia, endotracheal intubation, etc.

In general, laryngoscopy mainly examines the larynx, which can be partially examined or completely examined and needs to be determined according to the purpose of the examination. In addition to examination, laryngoscopy can also be used to assist in the performance of some surgeries. Laryngoscopes have two categories: direct laryngoscopes and indirect laryngoscopes, and there are many types if subdivided, such as direct laryngoscopes, which can also be divided into thin sheet laryngoscopes and direct laryngoscopes for lateral fissure. Different laryngoscopes are used differently, and the content of the examination varies, but in general, it is still to examine whether lesions occur in the larynx and whether there are foreign bodies.